Band arithmetic lets you combine spectral bands to highlight features; thresholding turns continuous values into simple classes. Together they power fast, interpretable analyses.
Learning objectives
- Compute simple band math (ratios, normalized differences) in Earth Engine.
- Apply thresholds to isolate features (vegetation, water, burn scars).
- Visualize band math outputs with sensible palettes and ranges.
- Know common pitfalls (scaling, band order, clouds).
Why it matters
These are the fastest tools to get actionable maps: one line to compute, one line to visualize, one threshold to extract what you need.
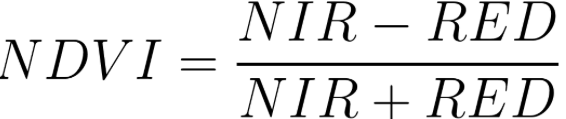
Quick win: NDVI + threshold
// Landsat 8 SR: scale and offset first
var img = ee.Image('LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_L2/LC08_044034_20210623')
.multiply(0.0000275).add(-0.2);
var ndvi = img.normalizedDifference(['SR_B5', 'SR_B4']).rename('NDVI');
Map.centerObject(img, 9);
Map.addLayer(ndvi, {min: 0, max: 0.8, palette: ['brown', 'yellow', 'green']}, 'NDVI');
// Threshold NDVI to flag healthy vegetation
var vegMask = ndvi.gte(0.4);
Map.addLayer(vegMask.updateMask(vegMask), {palette: ['00ff00']}, 'NDVI >= 0.4');What you should see
A green NDVI layer and a bright green mask highlighting pixels above the 0.4 threshold.
Other common band math recipes
- Simple ratio:
nir.divide(red)to compare two bands directly. - Water detection:
normalizedDifference(['GREEN','NIR'])(NDWI/MNDWI variants). - Burn severity:
normalizedDifference(['NIR','SWIR2'])(NBR).
Pro tips
- Use
.normalizedDifference()instead of manual math to avoid mistakes. - Mask clouds before computing indices to prevent spurious extreme values.
- Band numbers change by sensor; check the Data Catalog first.
Try it: quick experiments
Change the NDVI threshold to 0.2 and see how coverage expands.
Swap to Sentinel-2 (B8, B4) and re-run the NDVI + threshold flow.
Compute NBR and apply a threshold (for example, nbr.lt(0.1)) to flag burned areas.
Common mistakes
- Forgetting scale/offset on surface reflectance before math.
- Using incorrect band names for the chosen sensor.
- Applying thresholds without considering seasonality or clouds.
Quick self-check
- Why does NDVI range from -1 to 1?
- What does a threshold on NDVI actually select?
- Which bands would you use for NDWI on Sentinel-2?
This module builds on
- Image Collections - loading and selecting images
- Variables - storing intermediate results
Next steps
- NDVI - the most common vegetation index
- Spectral Indices - NDWI, EVI, and more
- Reducers - summarize mean NDVI over areas
- Classification - use indices as classifier features