At a Glance
At a Glance
🎯 Learning Outcomes
- Understand: Describe physical geography and the "Plateau Continent."
- Analyze: Examine colonial legacies and modern political borders.
- Understand: Explain the "Demographic Dividend" and rapid urbanization.
- Evaluate: Assess the Great Green Wall as a response to desertification.
🔑 Key Terms
Sahel, Great Rift Valley, Demographic Dividend, Berlin Conference (1884), Escarpment, Dual Economy, Desertification.
🛑 Stop & Check
Reveal Answer
⚡ Common Misconception
Myth: Sub-Saharan Africa is mostly jungle/rainforest.
Fact: The majority of the region is actually Savanna (grassland) or Steppe. The rainforest is concentrated only in the central Congo Basin.
🦠Regional Snapshot: Africa South of the Sahara
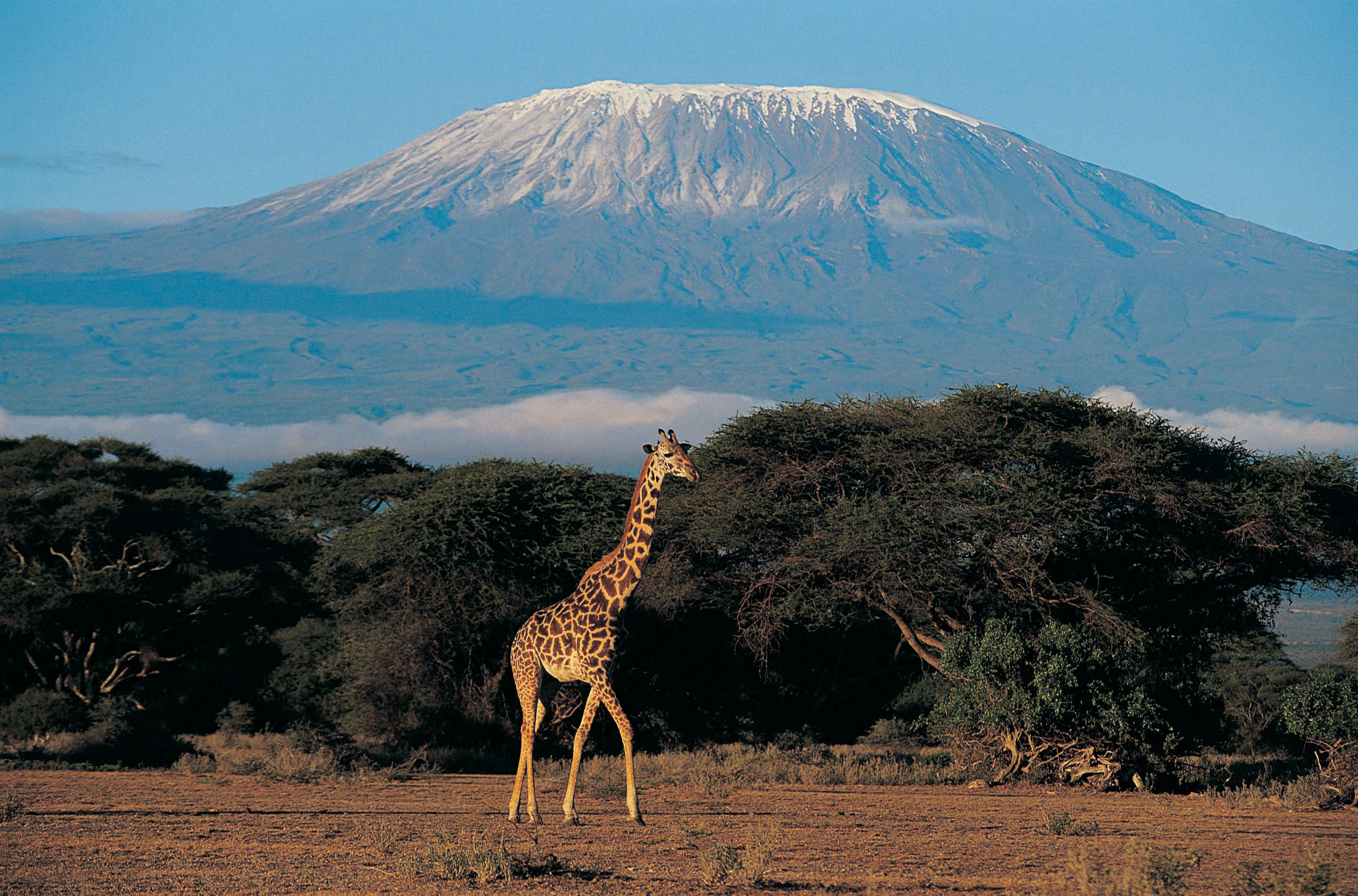
Sub-Saharan Africa is a region of immense potential and complex challenges. It contains some of the world's fastest-growing economies and its most youthful population. Geographically, it is a "continent of plateaus," where elevation and access to water define the limits of human activity.
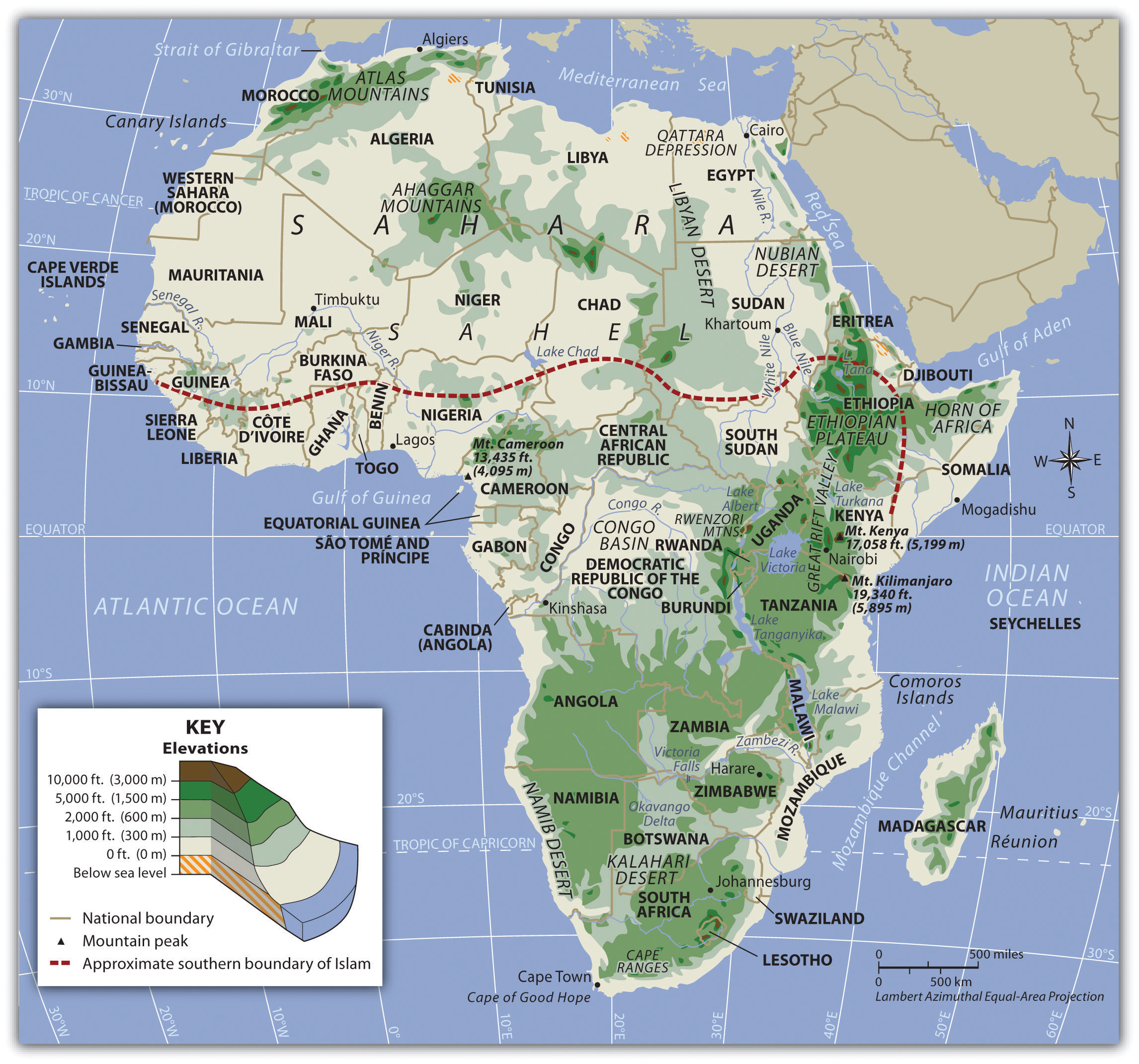
ðŸ—ºï¸ Interactive Map: The African Plateaus
Explore the Great Rift Valley, the Congo Basin, and the semi-arid Sahel. Zoom in to see the locations of rising megacities like Lagos, Kinshasa, and Nairobi.
Toggle between Physical terrain and Political boundaries. Notice the large number of landlocked states - a major geographic challenge for trade.
â›°ï¸ Physical Geography: Rifts, Basins, and Transitions
Africa's physical geography is unique for its extensive Plateau surfaces. The Great Rift Valley in the east is a massive geological fault where the continent is slowly pulling apart, creating some of the world's deepest lakes.

The Congo Basin contains the world's second-largest rainforest, while the Sahel represents a critical environmental and cultural transition zone currently threatened by desertification.
🔠Geographic Inquiry
Sub-Saharan Africa has few natural harbors and many waterfalls (escarpments) near its coasts. How did these physical features historically hinder European inland exploration and how do they still impact modern infrastructure costs?
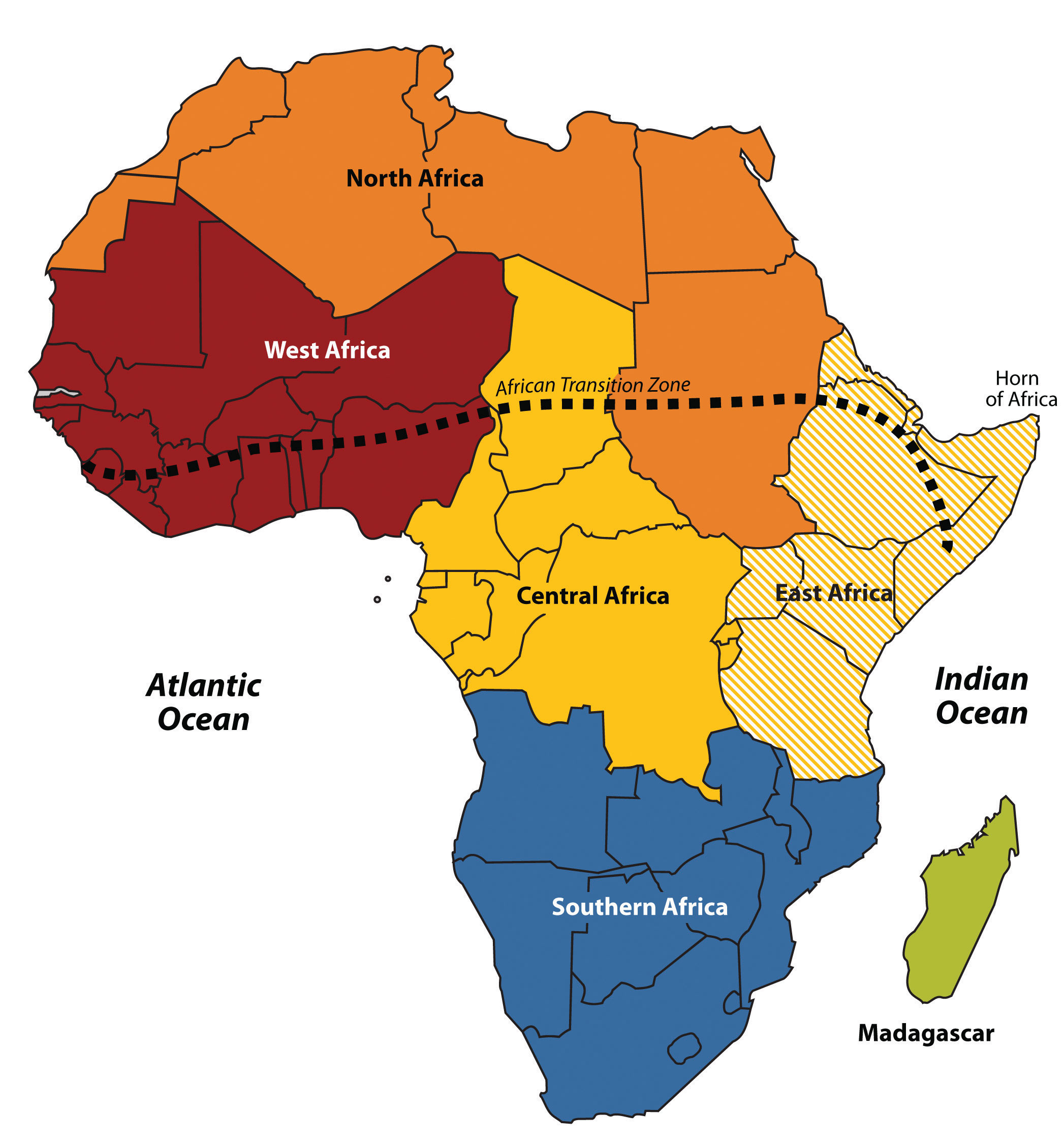
👥 Human Geography: Colonial Borders and Dual Economies
The contemporary political map of Africa was largely drawn at the Berlin Conference (1884), where European powers divided the continent without regard for existing ethnic or linguistic boundaries. This legacy of "arbitrary borders" remains a significant centrifugal force in the region.
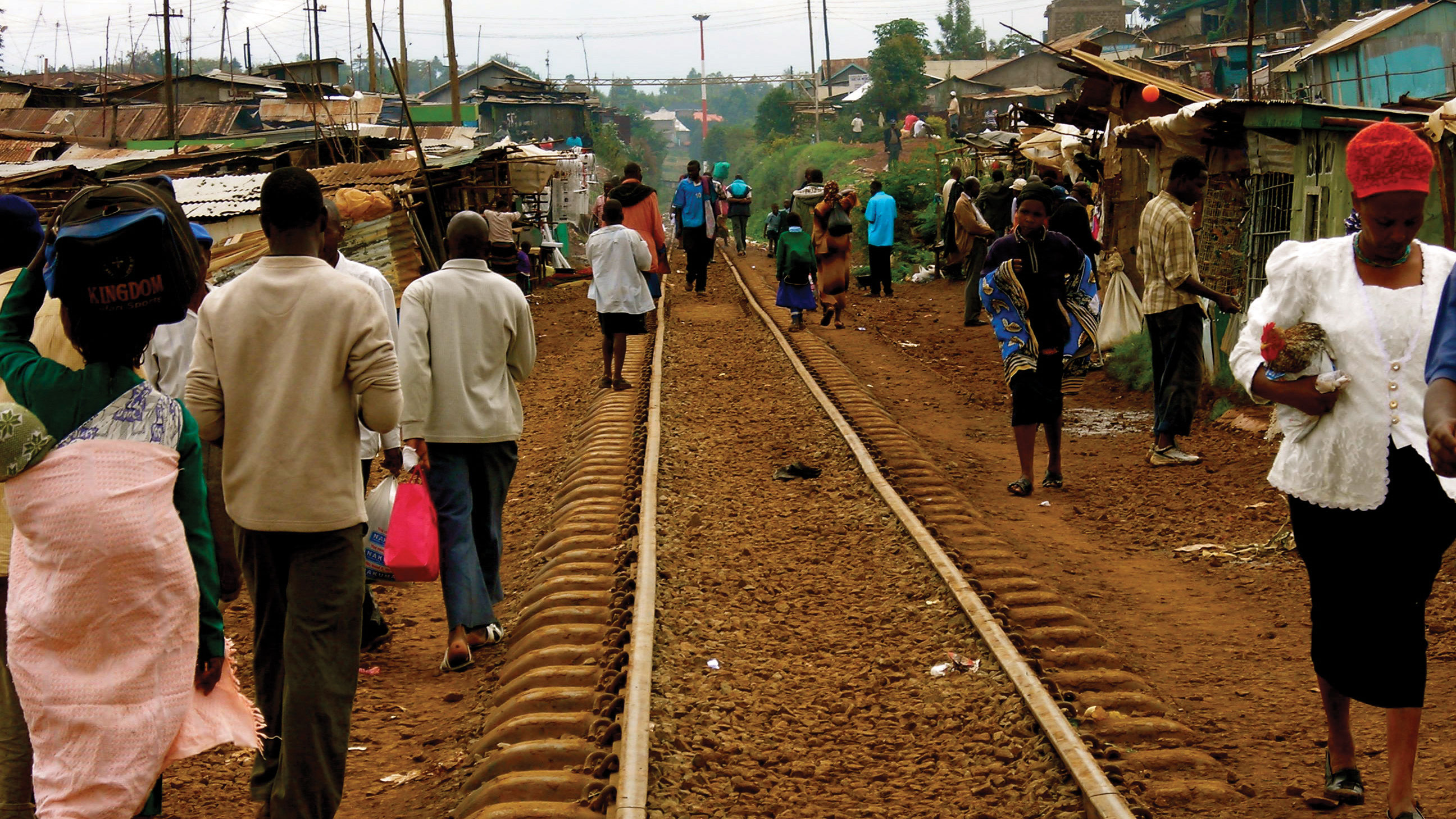

Most African cities operate as Dual Economies, with a formal sector of corporate and government jobs and a massive Informal Sector of street vending and small-scale services that employs up to 80% of the urban workforce.
The Great Green Wall: A Continental Shield
The "Great Green Wall" is a massive geographic project spanning 8,000 km across the Sahel. It aims to restore 100 million hectares of degraded land and sequester 250 million tons of carbon. It represents a proactive geographic solution to the combined threats of desertification and climate change.
Questions to Consider:
- Is the Great Green Wall a formal, functional, or perceptual region?
- How does this project illustrate the intersection of physical environmental management and human development?
- Sahel
- The semi-arid transition zone between the Sahara Desert and the tropical savannas.
- Demographic Dividend
- The economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population's age structure.
- Escarpment
- A steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion, separating two levels of differing elevation (common at the edges of Africa's plateaus).
- Africa is a "Continent of Plateaus" with high average elevations and significant interior rift systems.
- The colonial legacy of the Berlin Conference remains a primary factor in contemporary political and economic challenges.
- The region is the world's youngest and fastest-urbanizing, presenting both an immense developmental opportunity and an infrastructure crisis.
The Congo Basin: Whose Rainforest Is It?
The Congo Basin contains the world's second-largest tropical rainforest — a carbon sink critical to global climate stability. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) sits atop vast mineral wealth (cobalt, coltan, gold) essential for electric vehicles and smartphones. Yet the DRC is one of the world's poorest countries, wracked by decades of conflict. You are attending an international summit to negotiate a Congo Basin Conservation and Development Compact.
🇨🇩 Role A: Democratic Republic of Congo
You are home to 100 million people, most living in extreme poverty. Your forests and minerals are your only path to development. You argue that wealthy nations destroyed their own forests during industrialization — you should not be denied the same right. You demand payment for "ecosystem services" if you are to protect the forest.
🇪🇺 Role B: European Union
You have pledged billions in climate finance for forest protection. But you also need DRC's cobalt for your electric vehicle transition. You want binding conservation agreements but must address accusations that your "green" economy is built on exploited African resources.
🌿 Role C: Indigenous Forest Communities
Your communities have lived in and protected the Congo rainforest for millennia. Both the DRC government and foreign companies threaten your land rights. You want legal recognition of your territorial rights and veto power over any development or conservation projects on your land.
🌐 Role D: African Union Mediator
You want to ensure that any deal benefits African nations, not just foreign governments and corporations. You advocate for African-led conservation models and demand that mineral supply chains be processed within Africa to create local jobs and value.
💬 Discussion & Reflection Prompts
Reflect on Your Learning
- The Resource Curse: Many of Sub-Saharan Africa's richest countries in natural resources (DRC, Nigeria, Angola) have some of the highest poverty rates. How does geography — the location of resources and the colonial borders drawn around them — help explain this paradox?
- The Sahel's Triple Crisis: The Sahel region faces simultaneous climate change, desertification, and political instability. How do these geographic challenges reinforce each other, and what does this tell us about the relationship between environment and conflict?
- Urbanization Without Industrialization: African cities are growing faster than any other region, yet this urbanization is not accompanied by the same industrial development seen in Asia. What geographic and historical factors explain this difference?
Discuss With Your Peers
- Africa has 54 countries — more than any other continent — many with borders drawn by European colonizers with no regard for ethnic or geographic realities. How do these "artificial" borders continue to shape conflict and development today?
- The Great Green Wall initiative aims to plant an 8,000 km belt of trees across the Sahel to stop desertification. Is this a viable geographic solution, or does it ignore the political and economic root causes of land degradation?
- China has become Africa's largest trading partner and infrastructure investor. How does this new geographic relationship differ from European colonialism? What are the potential benefits and risks for African nations?
📊 Data Exploration: Human Development in Sub-Saharan Africa
The Human Development Index (HDI) measures a country's achievement in health, education, and income on a scale from 0 to 1. Compare HDI scores across selected Sub-Saharan African nations. Notice the dramatic variation within the region — and consider what geographic factors (landlocked vs. coastal, resource wealth, colonial history) might explain these differences.
Interpretation: Mauritius and South Africa rank significantly higher than Niger and Chad. How do geographic factors — coastline access, climate, mineral resources, and colonial borders — help explain this development gap within a single continent?
✅ Knowledge Check
Loading quiz questions...
📊 Curriculum Standards Alignment
This chapter aligns with the following National and State geography standards.
