At a Glance
At a Glance
🎯 Learning Outcomes
- Understand: Describe how the Ring of Fire shapes the hazard geography of Japan.
- Analyze: Examine the rise of the Asian Tigers and China's SEZs.
- Understand: Explain the geopolitical strategy of the Belt and Road Initiative.
- Evaluate: Assess the demographic crisis of aging populations in Japan and China.
- Apply: Apply geographic concepts to understand the Taiwan, Hong Kong, and DMZ conflicts.
🔑 Key Terms
Asian Tigers, Hukou System, Special Economic Zone (SEZ), Ring of Fire, State Capitalism, Tsunami, DMZ (Demilitarized Zone).
🛑 Stop & Check
Reveal Answer
⚡ Common Misconception
Myth: "Chinese" is one spoken language.
Fact: While Mandarin is the official language, there are hundreds of distinct dialects (like Cantonese, Wu, Min) that are mutually unintelligible. The written character system is what unifies the language across the region.
🯠Regional Snapshot: The Eastern Realm
East Asia is a region of superpowers. It contains the world's second and third largest economies (China and Japan) and some of its most ancient continuous civilizations. The geography ranges from the high Tibetan Plateau to the crowded archipelagos of Japan, all linked by the shared cultural thread of Confucianism.
ðŸ—ºï¸ Interactive Map: East Asia
Explore the diverse landscapes of the region. Zoom in to see the density of the Pearl River Delta megalopolis and the strategic location of the Taiwan Strait.
Toggle between Physical terrain and Political boundaries. Notice how Japan is an archipelago (chain of islands) situated directly on a tectonic plate boundary.
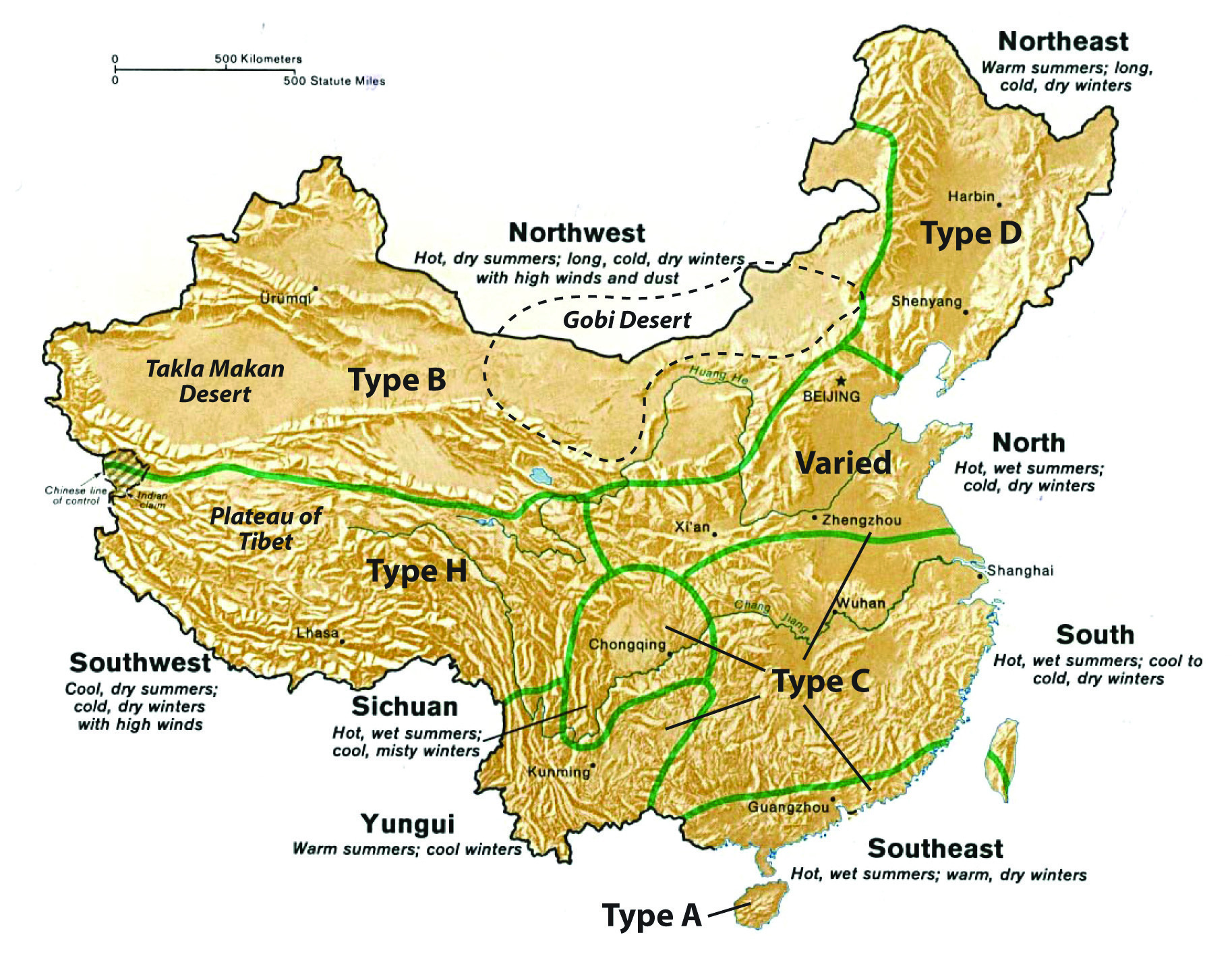
â›°ï¸ Physical Geography: Rivers and Rings
East Asia's physical geography is defined by two massive forces: the great river systems of China and the tectonic instability of the Pacific Rim.

The Yellow River (Huang He) and Yangtze River (Chang Jiang) have supported Chinese civilization for millennia. To the east, the island nations of Japan and Taiwan are shaped by volcanic activity.
🔠Geographic Inquiry
Japan has almost no natural resources (oil, iron, coal) yet became an industrial superpower. How did its geographic location as an island nation force it to develop a unique economic strategy based on trade and human capital?
👥 Human Geography: The Asian Tigers
The economic rise of East Asia is one of the defining stories of the 20th and 21st centuries. Following Japan's lead, the Asian Tigers (South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore) industrialized rapidly through export-oriented manufacturing.
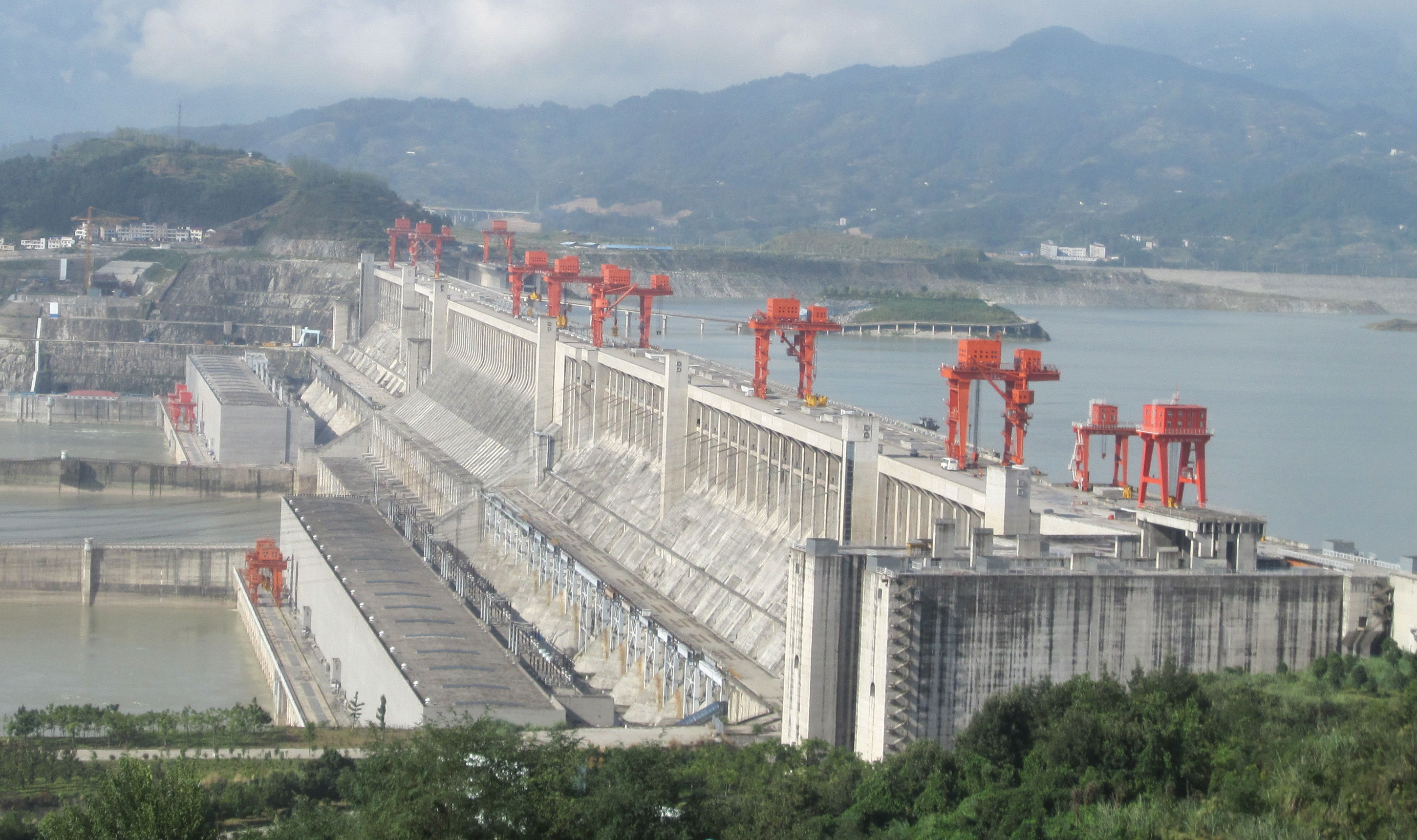

China followed suit with Special Economic Zones (SEZs) like Shenzhen, transforming from an agrarian society to the "factory of the world" in just one generation.
Taiwan: The Geopolitics of Semiconductors
Taiwan is a small island with an outsized impact on the world. It produces over 60% of the world's semiconductors and over 90% of the most advanced chips. This "Silicon Shield" makes Taiwan geographically indispensable to the global economy, yet its political status remains the most dangerous flashpoint in US-China relations.
Questions to Consider:
- How does Taiwan's physical geography (an island 100 miles off China's coast) shape its defense strategy?
- Is Taiwan a "functional region" integrated with China's economy, or a distinct political entity?
💡 Big Ideas: Flip to Explore
Click on the cards below to reveal the core geographic concepts for East Asia.
Special Economic Zones
Click to flip
Specific areas (like Shenzhen) where business and trade laws differ from the rest of the country. China used these to test capitalism and attract foreign investment.
Ring of Fire
Click to flip
The horseshoe-shaped zone around the Pacific Ocean where many earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. Japan sits directly on this volatile boundary.
Hukou System
Click to flip
China's household registration system that ties social services (schools, healthcare) to your place of birth, creating a divide between urban and rural citizens.
The South China Sea: Competing Claims in the Pacific
The South China Sea is one of the world's most strategically important waterways — carrying over $3 trillion in trade annually and sitting atop vast oil and gas reserves. China has built artificial islands and military installations on disputed reefs, claiming nearly the entire sea. Multiple nations dispute these claims. You are attending an ASEAN emergency summit to negotiate a Code of Conduct.
🇨🇳 Role A: China
You claim the South China Sea based on the "Nine-Dash Line," citing historical fishing rights going back centuries. Your island-building program is complete. You reject the 2016 international tribunal ruling against your claims and see this as a matter of national sovereignty.
🇵🇭 Role B: Philippines
China's artificial islands are within your Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Your fishermen are being blocked from traditional fishing grounds. You won the 2016 tribunal ruling but China ignores it. You need US support but also depend on Chinese investment.
🇻🇳 Role C: Vietnam
You have the longest history of conflict with China and the most to lose. You claim the Paracel and Spratly Islands and have your own island-building program. You want a strong multilateral agreement but must balance your economic ties with China.
🇺🇸 Role D: United States (Observer)
You conduct "Freedom of Navigation" operations in the disputed waters. You have mutual defense treaties with the Philippines. You see China's expansion as a threat to the rules-based international order, but you are not a party to the territorial disputes.
💬 Discussion & Reflection Prompts
Reflect on Your Learning
- The "East Asian Miracle": Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and China all achieved rapid economic development through export-led manufacturing. What geographic factors (location, coastlines, labor supply) enabled this model? Why hasn't it worked the same way in every region?
- One-Child Policy's Legacy: China's one-child policy (1980–2015) dramatically altered its population pyramid. What geographic and economic challenges does an aging, shrinking population create for a country of China's size?
- The Hukou System: China's household registration system ties social services to birthplace, creating barriers to rural-urban migration. How does this geographic control mechanism shape urbanization patterns differently from other countries?
Discuss With Your Peers
- Japan and South Korea are both island/peninsula nations with few natural resources, yet they became global economic powerhouses. How did their geographic position in the Pacific help them leverage trade relationships?
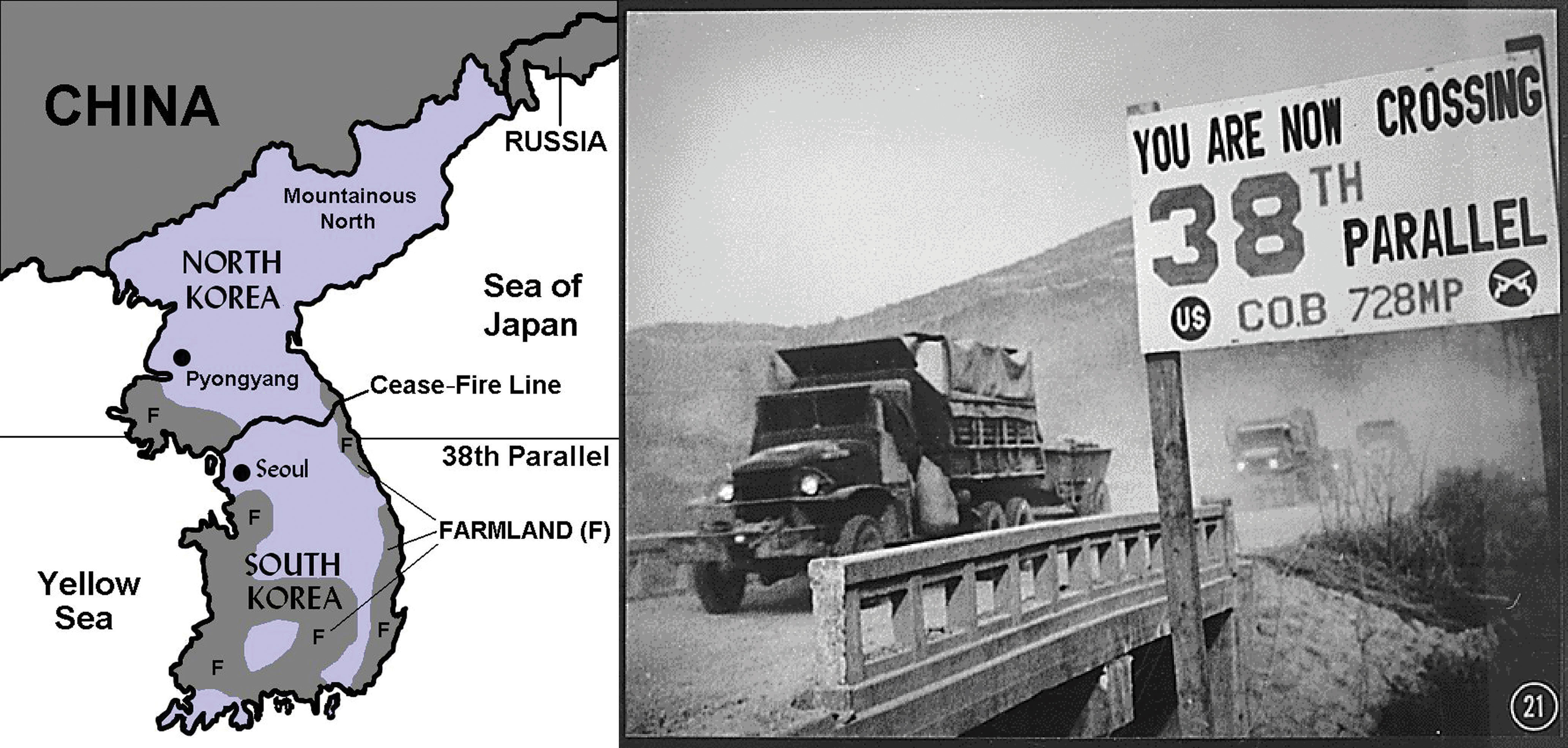
- North Korea is one of the most isolated countries on Earth. How does its mountainous terrain and geographic position between China and South Korea shape its political strategy of self-reliance (Juche)?
- China's Belt and Road Initiative is building infrastructure across Asia, Africa, and Europe. Is this modern economic geography, or a new form of geopolitical influence? How does geography determine which countries are most strategically important to China?
📊 Data Exploration: The East Asian Economic Miracle
East Asia's economic transformation over the past 50 years is one of the most dramatic in human history. The chart below compares GDP per capita (purchasing power parity, USD) for East Asian nations alongside the global average. Notice how Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan — all resource-poor island/peninsula nations — achieved extraordinary prosperity through trade and manufacturing.
Interpretation: Japan and South Korea have GDP per capita comparable to Western Europe, despite having almost no natural resources. North Korea, with similar geography and resources to South Korea, has one of the world's lowest GDPs. What does this tell us about the role of political geography (economic systems, trade openness) vs. physical geography in determining prosperity?
✅ Knowledge Check
Loading quiz questions...
📊 Curriculum Standards Alignment
This chapter aligns with the following National and State geography standards.